6e6713cc8cd7e99c40bec2a5c074b049bd381458
lightweight_charts_python
lightweight-charts-python aims to provide a simple and pythonic way to access and implement TradingView's Lightweight Charts.
Installation
pip install lightweight_charts
Features
- Simple and easy to use.
- Blocking or non-blocking GUI.
- Streamlined for live data, with methods for updating directly from tick data.
- Support for PyQt and wxPython.
- Multi-Pane Charts using the
SubChart(examples).
1. Display data from a csv:
import pandas as pd
from lightweight_charts import Chart
if __name__ == '__main__':
chart = Chart()
# Columns: | time | open | high | low | close | volume (if volume is enabled) |
df = pd.read_csv('ohlcv.csv')
chart.set(df)
chart.show(block=True)
2. Updating bars in real-time:
import pandas as pd
from time import sleep
from lightweight_charts import Chart
if __name__ == '__main__':
chart = Chart()
df1 = pd.read_csv('ohlcv.csv')
df2 = pd.read_csv('next_ohlcv.csv')
chart.set(df1)
chart.show()
last_close = df1.iloc[-1]
for i, series in df2.iterrows():
chart.update(series)
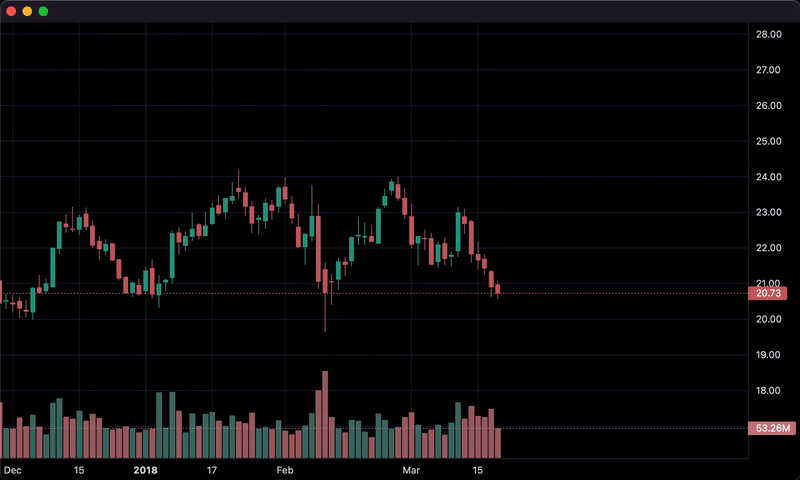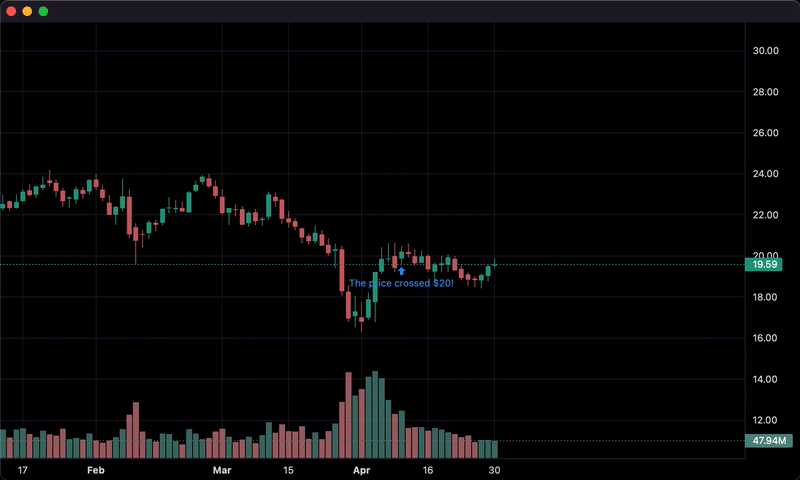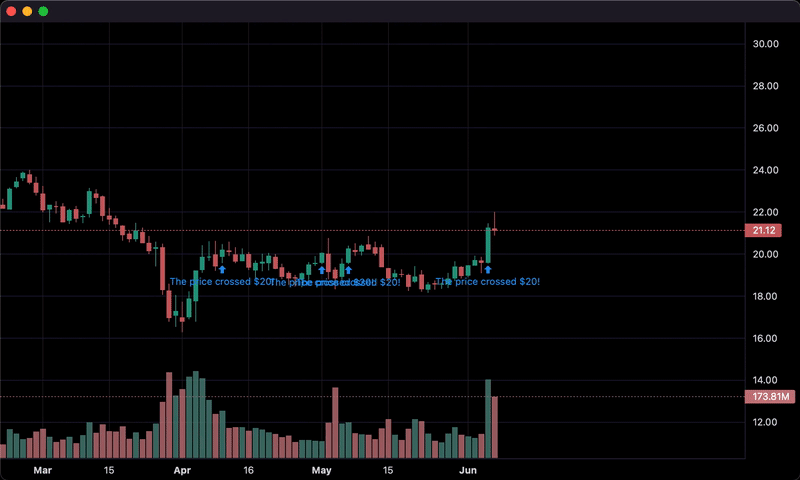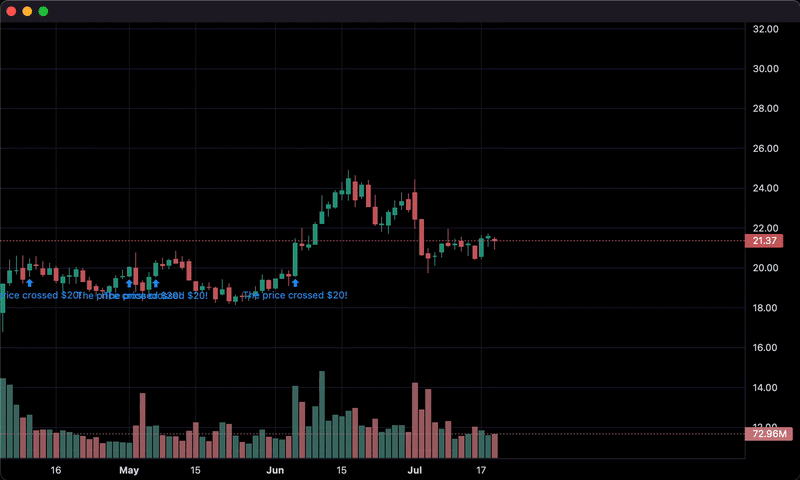
if series['close'] > 20 and last_close < 20:
chart.marker(text='The price crossed $20!')
last_close = series['close']
sleep(0.1)
3. Updating bars from tick data in real-time:
import pandas as pd
from time import sleep
from lightweight_charts import Chart
if __name__ == '__main__':
df1 = pd.read_csv('ohlc.csv')
# Columns: | time | price | volume (if volume is enabled) |
df2 = pd.read_csv('ticks.csv')
chart = Chart(volume_enabled=False)
chart.set(df1)
chart.show()
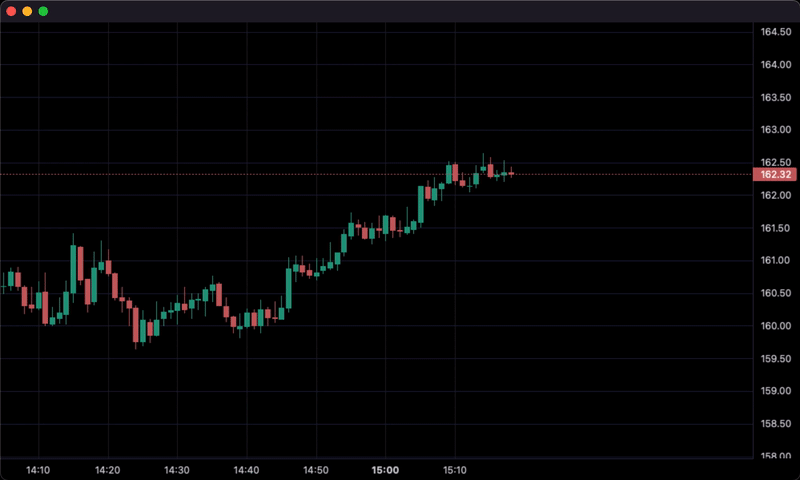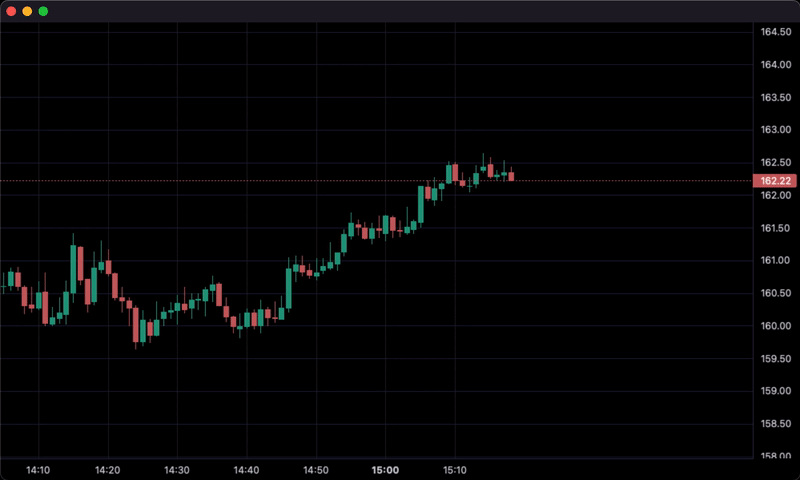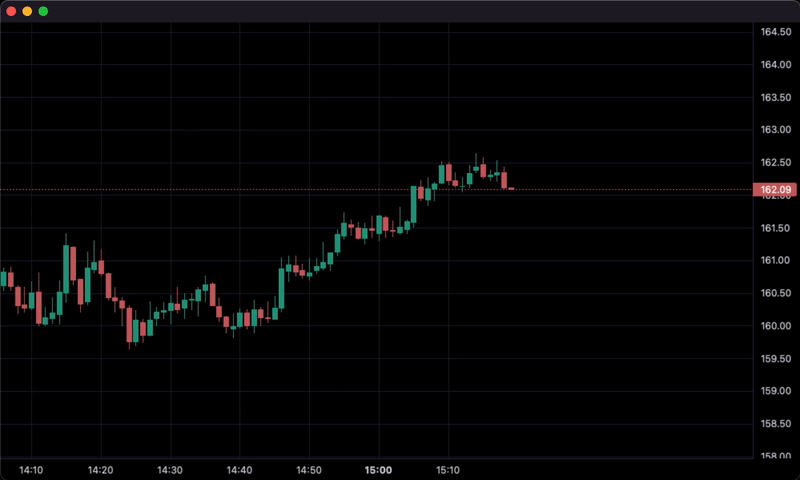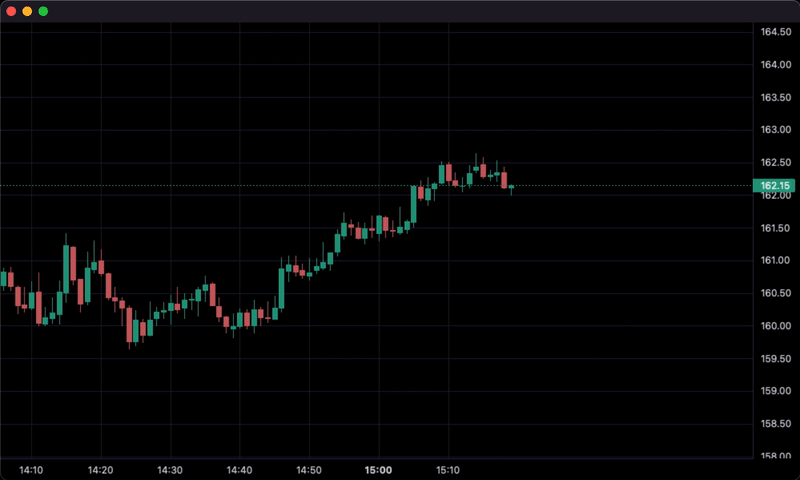
for i, tick in df2.iterrows():
chart.update_from_tick(tick)
sleep(0.3)
4. Line Indicators:
import pandas as pd
from lightweight_charts import Chart
def calculate_sma(data: pd.DataFrame, period: int = 50):
def avg(d: pd.DataFrame):
return d['close'].mean()
result = []
for i in range(period - 1, len(data)):
val = avg(data.iloc[i - period + 1:i])
result.append({'time': data.iloc[i]['date'], 'value': val})
return pd.DataFrame(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
chart = Chart()
df = pd.read_csv('ohlcv.csv')
chart.set(df)
line = chart.create_line()
sma_data = calculate_sma(df)
line.set(sma_data)
chart.show(block=True)
5. Styling:
import pandas as pd
from lightweight_charts import Chart
if __name__ == '__main__':
chart = Chart(debug=True)
df = pd.read_csv('ohlcv.csv')
chart.layout(background_color='#090008', text_color='#FFFFFF', font_size=16,
font_family='Helvetica')
chart.candle_style(up_color='#00ff55', down_color='#ed4807',
border_up_color='#FFFFFF', border_down_color='#FFFFFF',
wick_up_color='#FFFFFF', wick_down_color='#FFFFFF')
chart.volume_config(up_color='#00ff55', down_color='#ed4807')
chart.watermark('1D', color='rgba(180, 180, 240, 0.7)')
chart.crosshair(mode='normal', vert_color='#FFFFFF', vert_style='dotted',
horz_color='#FFFFFF', horz_style='dotted')
chart.legend(visible=True, font_size=14)
chart.set(df)
chart.show(block=True)
6. Callbacks:
import pandas as pd
from lightweight_charts import Chart
def on_click(bar: dict):
print(f"Time: {bar['time']} | Close: {bar['close']}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
chart = Chart()
df = pd.read_csv('ohlcv.csv')
chart.set(df)
chart.subscribe_click(on_click)
chart.show(block=True)
Description
Languages
Python
53.9%
TypeScript
42%
CSS
3.1%
HTML
0.5%
Shell
0.3%
Other
0.2%